|
|
 |
 |
 |
| ‘@Purpose@‘ |
| Case of Ur |
 |
 |
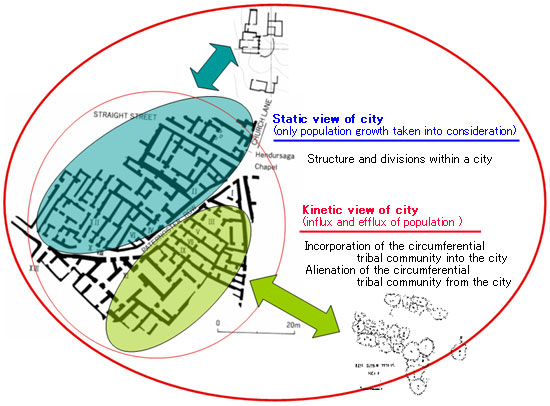
This is a map of the ancient city of
Ur in southern Mesopotamia during the Isin-Larsa period.
Not restricted
to Ur, each block of the ancient cities in this region shows different
styles in architectures and daily necessities.
The differentiation
within the city has been explained so far as a result of stratification
and the division within the city community.
This interpretation
is based on what we call gstatic viewh, which only takes population
growth within a city into consideration. However, it interprets
a city as a closed system.
Then, what if we interpret a city in a more integrated way in
relation to the circumference communities? Since a city is always
surrounded
by, for example, small scale villages, camps of nomadic tribes,
it is possible to study the interrelationships between city and
circumference by comparing them.
For example, we may observe a
corresponding relation between a certain area of the city and circumferential
villages, or incorporation of nomadic tribes of another area into
a city, and so on.
Thus, the focus of this research is to reconsider
the Middle Eastern societies in a more inclusive way, incorporating
mobility factors, such as influx or efflux of the nomads, that
contributed to the development of the city. |
 |
|
| @ |
|
 |
| |
| Copyright (C) 2005-2007 Kokushikan University |
|
|

